Tilting Check Valve vs. Rubber Flap Check Valve: A Detailed Comparison of Their Strengths and Weaknesses
When selecting a Check Valve for your piping system, it's important to understand the differences between thetilting Check Valve and the rubber flap Check Valve. While both valves serve the purpose of preventing reverse flow, they have distinct features, advantages, and limitations depending on your system's needs. In this article, we’ll compare both valve types based on key aspects such as design, performance, installation, and maintenance to help you choose the best option for your system.
1. Valve Design and Mechanism
Tilting Check Valve:
The tilting Check Valve features a large eccentric inclined disc, which enables smooth operation and provides a two-stage closing action to prevent water hammer. The design allows for an adjustable slow closing time, making it versatile for various applications.
Rubber Flap Check Valve:
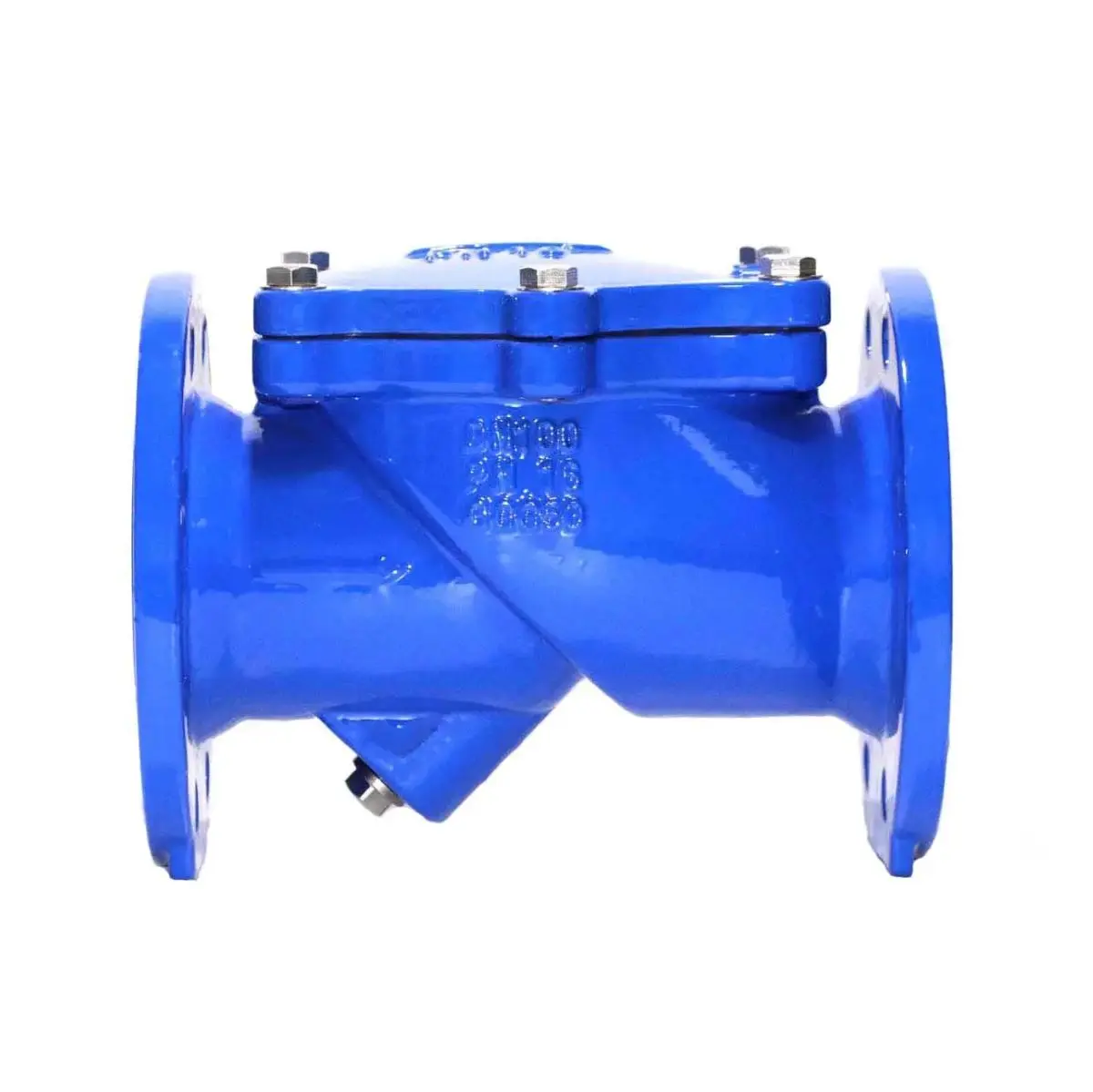
The rubber flap Check Valve is simpler in design, using a rubber flap that swings to prevent backflow. This valve is usually composed of fewer moving parts and relies on the fluid’s pressure to open or close the flap.
Comparison:
Tilting Check Valve: More complex with advanced features such as a two-stage closing mechanism that reduces water hammer. It’s ideal for systems where controlling the speed of valve closure is essential.
Rubber Flap Check Valve: Simpler and more straightforward, with a basic rubber flap that automatically closes when reverse flow occurs. This simplicity makes it easy to use, but it lacks the advanced water hammer control of the tilting valve.
Winner:
The tilting Check Valve offers superior design features, particularly for applications requiring fine control of water hamme
2. Sealing Efficiency
Tilting Check Valve:
The tilting check valve uses a soft seal with high-quality sealing rings that ensure zero leakage and excellent sealing performance. It’s highly reliable in preventing backflow, even under high-pressure conditions.
Rubber Flap Check Valve:
The rubber flap provides 100% sealing when the valve is closed, utilizing a resilient rubber material for effective backflow prevention. The valve is generally efficient in low-pressure systems but may not be as reliable in high-pressure applications over time.
Comparison:
Tilting Check Valve: Provides better sealing, particularly in high-pressure conditions. Its sealing performance is highly reliable over a long service life.
Rubber Flap Check Valve: Excellent for preventing backflow in most systems but may struggle in high-pressure or more demanding environments where rubber wear could lead to leaks.
Winner:
The tilting check valve excels in sealing efficiency, especially under varied and high-pressure conditions.
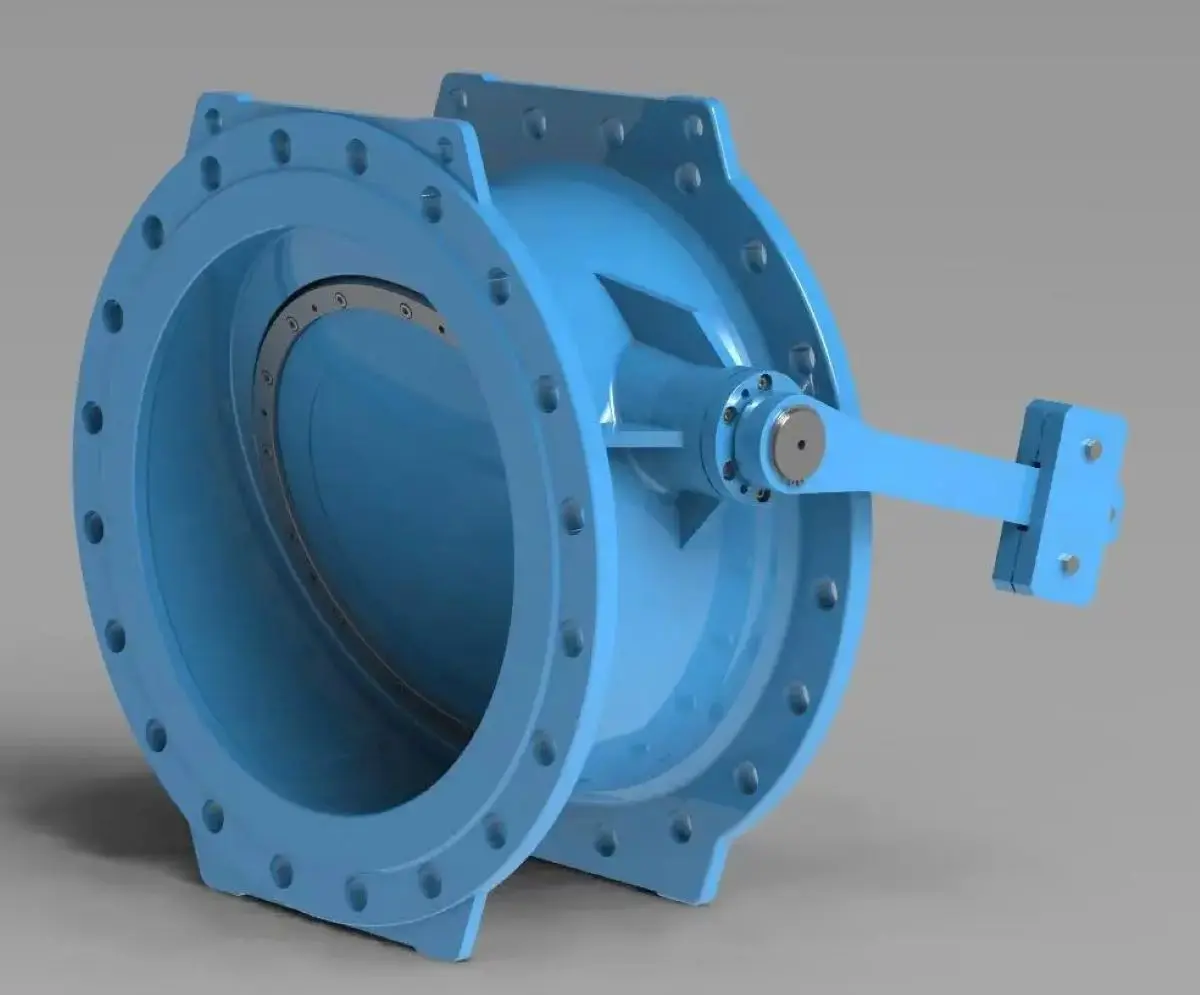
3. Durability and Maintenance
Tilting Check Valve:
This valve is designed with self-lubricating bearings and a robust seal, making it durable and reliable in the long run. However, its complex design can lead to more maintenance requirements, especially if the adjustable two-stage closure mechanism needs servicing.
Rubber Flap Check Valve:
The rubber flap check valve has fewer moving parts, which translates to lower maintenance. The rubber flap can wear out over time, especially if there is frequent reverse flow. However, the valve is generally easier to maintain and replace than the more complex tilting check valve.
Comparison:
Tilting Check Valve: Offers a long lifespan but may require more frequent maintenance due to its complex components.
Rubber Flap Check Valve: Low-maintenance with simple design, but the rubber flap may need replacement after extended use.
Winner:
The rubber flap check valve wins in terms of ease of maintenance, while the tilting check valve excels in long-term durability.
4. Flow Resistance and Energy Efficiency
Tilting Check Valve:
The large eccentric disc design of the tilting check valve results in lower flow resistance, making it highly efficient in terms of energy consumption. It’s designed to minimize friction, which reduces pressure drops in the system.
Rubber Flap Check Valve:
This valve has a fully encapsulated rubber flap that allows for an unrestricted flow area when open. However, the design can result in slightly higher flow resistance compared to the tilting check valve, leading to a minor increase in energy consumption.
Comparison:
Tilting Check Valve: Lower flow resistance, contributing to greater energy efficiency in high-flow systems.
Rubber Flap Check Valve: While it offers an unrestricted flow area, the rubber flap design may introduce slightly more resistance compared to the tilting valve.
Winner:
The tilting check valve offers better energy efficiency due to its design, especially in high-flow applications.

5. Cost and Installation
Tilting Check Valve:
The tilting check valve is more expensive due to its advanced features and design complexity. Installation can be more involved, especially in systems that require fine-tuning of the two-stage closing mechanism.
Rubber Flap Check Valve:
This valve is more affordable and easier to install due to its simpler design. It is a more cost-effective solution for basic systems that don’t require advanced water hammer control.
Comparison:
Tilting Check Valve: Higher upfront cost and more complex installation but suitable for more specialized, high-performance systems.
Rubber Flap Check Valve: More affordable and easier to install, making it a good option for systems with less demanding requirements.
Winner:
The rubber flap check valve is the winner in terms of cost and ease of installation, while the tilting check valve justifies its higher cost with advanced features.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both the tilting check valve and the rubber flap check valve offer unique advantages depending on your system’s needs. If you require advanced features like water hammer control, durability, and high-pressure sealing, the tilting check valve is the better choice. However, for simpler, low-maintenance systems with a focus on cost-effectiveness, the rubber flap check valve is an excellent option.
By comparing these two valves based on their design, sealing efficiency, durability, and more, you can make a well-informed decision that best suits your application.